Azure Portal: 7 Ultimate Power Tips to Master Microsoft’s Cloud
Welcome to the world of cloud computing, where the Azure Portal reigns as a powerful gateway to managing your digital infrastructure. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, mastering this platform can transform how you deploy, monitor, and scale resources—fast, efficiently, and securely.
What Is the Azure Portal and Why It Matters

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services and resources across the Azure platform. It provides a centralized dashboard where users can create, configure, monitor, and optimize cloud assets such as virtual machines, databases, networking components, and AI tools—all from a single, intuitive environment.
A Unified Interface for Cloud Management
Unlike command-line tools or APIs, the Azure Portal offers a visual, user-friendly experience. It’s designed for both technical and non-technical users, enabling teams to collaborate more effectively. From launching a simple virtual machine to orchestrating complex multi-region deployments, the portal simplifies the entire lifecycle of cloud resources.
- Drag-and-drop dashboards for custom monitoring
- Real-time metrics and alerts
- Integrated billing and cost analysis tools
“The Azure Portal is the control center of your cloud journey—where strategy meets execution.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
How Azure Portal Compares to Other Cloud Dashboards
When stacked against AWS Management Console or Google Cloud Console, the Azure Portal stands out for its deep integration with Microsoft 365, Active Directory, and hybrid cloud environments. This makes it especially powerful for enterprises already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Tighter integration with Windows Server and SQL Server
- Superior support for hybrid deployments (on-premises + cloud)
- Advanced role-based access control (RBAC) with Azure AD
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface Like a Pro
Once you log in to the Azure Portal, the first thing you’ll notice is the clean, modular layout. Understanding its core components is essential to unlocking its full potential.
Dashboard and Hub Menu
The left-hand navigation pane, known as the Hub Menu, is your gateway to all Azure services. From here, you can access everything: Compute, Networking, Storage, Security, and more. The dashboard, on the other hand, is fully customizable—users can pin frequently used resources, charts, and monitoring widgets.
- Pin resource groups, VMs, or cost trends for quick access
- Create multiple dashboards for different teams (e.g., Dev, Ops, Finance)
- Use Quickstart templates directly from the dashboard
Search, Filters, and Resource Discovery
The global search bar at the top is one of the most underutilized yet powerful features in the Azure Portal. You can search by resource name, type, tag, or even region. Filters allow you to narrow down results by subscription, resource group, or status.
- Use wildcards and partial names for faster searches
- Save common filter combinations as favorites
- Leverage tags to organize resources across departments or projects
Setting Up Your First Azure Environment
Getting started with the Azure Portal begins with setting up your environment correctly. This includes configuring subscriptions, creating resource groups, and establishing governance policies from day one.
Understanding Subscriptions and Tenants
A subscription in the Azure Portal is a logical container for resources that are billed together. Each subscription is linked to an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant, which manages user identities and access. Organizations often use multiple subscriptions to separate environments (e.g., Dev, Test, Production) or departments.
- Free trial, Pay-As-You-Go, and Enterprise agreements offer different capabilities
- Each subscription has spending limits and service quotas
- Use Management Groups to apply policies across multiple subscriptions
Creating and Organizing Resource Groups
Resource groups are fundamental to organizing your cloud infrastructure. They act as containers for related resources—like a web app, its database, and associated networking components. Proper grouping ensures easier management, access control, and cost tracking.
- Name resource groups with a consistent convention (e.g., rg-prod-web-eastus)
- Apply tags for cost allocation (e.g., Department: Marketing, Environment: Production)
- Delete entire environments by removing the resource group
Deploying and Managing Virtual Machines via Azure Portal
One of the most common tasks in the Azure Portal is deploying virtual machines (VMs). Whether you’re running Linux or Windows workloads, the portal streamlines the process with guided wizards and pre-configured images.
Step-by-Step VM Creation
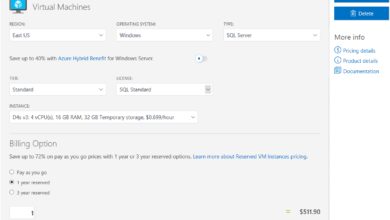
To create a VM, navigate to the Virtual Machines service, click Create, and follow the wizard. You’ll choose the OS image, VM size, authentication method, and networking settings. The Azure Portal also suggests cost-optimized SKUs based on your usage patterns.
- Select from marketplace images (Ubuntu, CentOS, Windows Server, etc.)
- Enable auto-shutdown to reduce costs
- Integrate with Azure Backup and Monitoring during setup
Monitoring and Scaling VMs
Once deployed, the Azure Portal provides real-time performance data through the Metrics tab. You can set up alerts for CPU, memory, or disk usage. For scaling, use Azure Autoscale to automatically add or remove VM instances based on demand.
- View CPU, network, and disk I/O graphs
- Create alert rules that trigger emails or webhooks
- Scale out using Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS)
Managing Storage and Databases in the Azure Portal
Storage and databases are the backbone of any cloud application. The Azure Portal offers seamless tools to manage Blob Storage, File Shares, SQL Databases, and Cosmos DB—all from a single pane of glass.
Configuring Azure Blob and File Storage
Azure Blob Storage is ideal for unstructured data like images, videos, and backups. Through the Azure Portal, you can create storage accounts, set access tiers (Hot, Cool, Archive), and manage shared access signatures (SAS) for secure file sharing.
- Use lifecycle management policies to auto-move data to cheaper tiers
- Enable soft delete to recover accidentally removed blobs
- Monitor storage usage and transaction costs
Creating and Monitoring Azure SQL Databases
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service. From the Azure Portal, you can deploy a new SQL server, configure firewall rules, set up geo-replication, and monitor performance with built-in dashboards.
- Choose between serverless and provisioned compute tiers
- Enable Threat Detection and Advanced Data Security
- Use Query Performance Insight to identify slow queries
Securing Your Cloud with Azure Portal’s Identity and Access Tools
Security is not an afterthought in the Azure Portal—it’s built in. With Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), and security recommendations, you can enforce least-privilege access across your environment.
Managing Users and Roles with Azure AD
Azure AD is the identity backbone of the Azure Portal. You can create users, assign licenses, and manage group memberships directly from the portal. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies add an extra layer of protection.
- Invite external users (B2B collaboration) securely
- Assign roles like Owner, Contributor, or Reader at subscription or resource level
- Use Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for just-in-time access
Using Azure Security Center and Defender
Azure Security Center (now part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud) provides a unified security management and advanced threat protection service. The Azure Portal integrates it seamlessly, offering security scores, vulnerability assessments, and remediation steps.
- Get a security score and track improvements over time
- Enable Defender for Servers, Storage, and SQL
- Respond to threats with automated playbooks
Optimizing Costs and Usage with Azure Portal Tools
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is cost control. The Azure Portal provides powerful tools like Cost Management, Budgets, and Advisor recommendations to help you optimize spending without sacrificing performance.
Tracking Spending with Cost Management
The Cost Management + Billing section in the Azure Portal gives you detailed insights into your usage and expenses. You can break down costs by resource, service, department, or tag. Visual charts and exportable reports make it easy to share data with finance teams.
- Set up budgets with alert thresholds (e.g., 80% of limit)
- Forecast future spending based on historical trends
- Compare actual vs. reserved instance usage
Leveraging Azure Advisor for Optimization
Azure Advisor is your personal cloud consultant. It analyzes your environment and provides actionable recommendations across five pillars: Cost, Performance, High Availability, Security, and Operational Excellence.
- Identify underutilized VMs and resize them
- Enable auto-shutdown for non-production resources
- Recommend reserved instances to save up to 72% on compute
Automating Tasks with Azure Portal’s Built-In Tools
While the Azure Portal is known for its GUI, it also supports automation through templates, runbooks, and integration with Azure CLI and PowerShell. This allows you to maintain consistency and reduce manual errors.
Using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Templates
ARM templates are JSON files that define your infrastructure as code (IaC). You can deploy them directly from the Azure Portal, enabling repeatable, version-controlled deployments. This is especially useful for DevOps teams.
- Deploy complex environments with a single click
- Use template specs to share approved templates across teams
- Validate templates before deployment to catch errors early
Scheduling Tasks with Azure Automation
Azure Automation allows you to run PowerShell or Python scripts (runbooks) on a schedule. From the Azure Portal, you can create, test, and monitor runbooks that automate routine tasks like patching, backups, or cleanup.
- Schedule VM shutdowns during weekends
- Automate user provisioning based on HR events
- Integrate with Logic Apps for workflow automation
Best Practices for Using the Azure Portal Effectively
To get the most out of the Azure Portal, it’s important to follow proven best practices. These include organizing resources logically, applying governance policies, and training your team on key features.
Implementing Naming Conventions and Tagging
Consistent naming and tagging are critical for manageability and cost tracking. Use prefixes for resource types (e.g., vm-, stg-, sql-) and apply tags like Environment, Owner, and Cost Center.
- Enforce naming policies using Azure Policy
- Use tags for chargeback and showback reporting
- Automate tagging during resource creation
Using Management Groups for Scalable Governance
For large organizations, Management Groups provide a hierarchical structure to apply policies and RBAC across multiple subscriptions. This simplifies governance and ensures compliance at scale.
- Apply a single policy to block public storage endpoints across all dev subscriptions
- Delegate access at the management group level
- Monitor compliance status across all child scopes
What is the Azure Portal?
The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud resources on Azure. It allows users to deploy, monitor, and manage services like virtual machines, storage, databases, and networking through a graphical dashboard.
How do I access the Azure Portal?
You can access the Azure Portal by visiting https://portal.azure.com and signing in with your Microsoft account or Azure Active Directory credentials. Access requires an active Azure subscription.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, the Azure Portal interface itself is free to access. However, the cloud resources you create and manage through it (like VMs, storage, and databases) incur costs based on usage. Microsoft offers a free tier and a $200 credit for new users.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Absolutely. While the Azure Portal is GUI-driven, it supports automation via ARM templates, Azure CLI, PowerShell, and Azure Automation runbooks. You can also use Logic Apps and Event Grid for workflow automation.
How secure is the Azure Portal?
The Azure Portal is built with enterprise-grade security, including integration with Azure AD, multi-factor authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and Microsoft Defender for Cloud. It complies with global standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Mastering the Azure Portal is no longer optional—it’s essential for anyone managing cloud infrastructure today. From deploying virtual machines to securing identities and optimizing costs, this powerful platform offers everything you need in one place. By leveraging its intuitive interface, robust security tools, and automation capabilities, you can streamline operations, reduce risks, and drive innovation across your organization. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your skills, the Azure Portal remains the ultimate command center for your cloud journey.
Further Reading: