MS Azure: 7 Powerful Reasons to Choose Microsoft’s Cloud
MS Azure isn’t just another cloud platform—it’s a game-changer. With unmatched scalability, enterprise-grade security, and seamless integration with Microsoft tools, it’s no wonder millions trust Azure for their digital transformation.
What Is MS Azure and Why It Matters

Microsoft Azure, commonly referred to as MS Azure, is a comprehensive cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft. Launched in 2010, it has rapidly evolved into one of the top three cloud providers globally, alongside Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). MS Azure offers over 200 services, including computing, analytics, storage, networking, and machine learning, enabling businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications across a global network of data centers.
History and Evolution of MS Azure
Azure began as Windows Azure in 2008, primarily focused on application hosting. By 2010, it officially launched with a broader vision: to deliver cloud-based services for businesses of all sizes. Over the years, Microsoft invested billions into expanding its infrastructure, acquiring companies like GitHub and Nuance, and integrating AI and hybrid cloud capabilities. Today, Azure powers over 95% of Fortune 500 companies, proving its dominance in enterprise environments.
- 2008: Announced as Windows Azure
- 2010: Official public launch
- 2014: Rebranded to Microsoft Azure
- 2020s: Expansion into AI, edge computing, and quantum computing
This evolution reflects Microsoft’s strategic shift from a software-centric company to a cloud-first, AI-driven organization.
Core Components of MS Azure
MS Azure is built on a modular architecture, allowing users to pick and choose services based on their needs. The core components include:
- Compute: Virtual machines, containers, serverless functions (Azure Functions), and batch processing.
- Storage: Blob storage, file shares, disk storage, and data lakes for structured and unstructured data.
- Networking: Virtual networks, load balancers, DNS, and content delivery networks (CDN).
- Databases: Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB (globally distributed NoSQL), and MySQL/PostgreSQL as managed services.
- Security & Identity: Azure Active Directory (AAD), Key Vault, and Security Center for threat detection.
These components work together to create a flexible, secure, and scalable environment for modern applications.
“Azure is not just infrastructure; it’s a platform for innovation.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
MS Azure vs. AWS vs. Google Cloud: A Comparative Analysis
When choosing a cloud provider, businesses often compare MS Azure with AWS and Google Cloud. While all three offer robust services, key differences influence decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations align their cloud strategy with business goals.
Market Share and Global Reach
As of 2024, AWS leads the market with approximately 32% share, followed by MS Azure at 23%, and Google Cloud at 10% (Synergy Research Group). However, Azure’s growth rate is the fastest among the three, especially in hybrid cloud and enterprise sectors. Azure operates in 60+ regions worldwide, more than any other cloud provider, ensuring low-latency access and compliance with local data regulations.
Its global presence is critical for multinational corporations needing data sovereignty. For example, Azure has specific regions in Germany, China, and the UAE managed by local partners to comply with strict data laws.
Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
One of MS Azure’s biggest advantages is its deep integration with Microsoft products like Windows Server, Active Directory, Office 365, and Dynamics 365. Organizations already using Microsoft tools find Azure a natural extension. For instance, Azure Active Directory enables single sign-on (SSO) across Microsoft 365 and third-party apps, simplifying identity management.
Additionally, Azure supports hybrid environments through services like Azure Arc and Azure Stack, allowing companies to manage on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud resources from a single control plane. This is a significant differentiator compared to AWS and GCP, which lack native integration with enterprise productivity suites.
Pricing and Cost Management
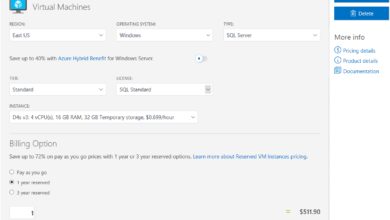
MS Azure uses a pay-as-you-go model, similar to competitors, but offers unique pricing benefits. For example, enterprises with Microsoft Enterprise Agreements (EA) can apply existing licenses to Azure services, reducing costs through the Azure Hybrid Benefit. This allows customers to use their on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses in the cloud with up to 40% savings.
Azure also provides detailed cost management tools like Azure Cost Management + Billing, which offers real-time spending insights, budget alerts, and recommendations for optimizing resource usage. Third-party tools like CloudHealth and Turbonomic integrate seamlessly for advanced financial operations (FinOps).
Key Services Offered by MS Azure
MS Azure’s service portfolio is vast, but some stand out due to their popularity, innovation, and business impact. These services form the backbone of modern cloud architectures and enable digital transformation across industries.
Azure Virtual Machines and Compute Options
Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) are one of the most widely used services, offering resizable compute capacity in the cloud. Users can deploy VMs running Windows, Linux, or specialized workloads like SAP and Oracle. VMs come in various sizes—from basic to GPU-optimized for AI training.
Beyond VMs, Azure offers alternative compute models:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Managed Kubernetes for container orchestration.
- Azure App Service: Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) for web apps without managing infrastructure.
- Azure Functions: Serverless computing for event-driven code execution.
These options provide flexibility for developers and IT teams to choose the right abstraction level for their applications.
Azure Blob Storage and Data Management
Azure Blob Storage is a scalable object storage solution ideal for unstructured data like images, videos, logs, and backups. It supports three access tiers—Hot, Cool, and Archive—allowing cost optimization based on data retrieval frequency.
For structured data, Azure offers:
- Azure SQL Database: Fully managed relational database with built-in high availability and AI-powered performance tuning.
- Azure Cosmos DB: Globally distributed, multi-model NoSQL database with single-digit millisecond latency at the 99th percentile.
- Azure Data Lake: Big data analytics platform for processing petabytes of data using tools like Azure Databricks and Synapse Analytics.
These services enable organizations to store, process, and analyze data at scale, supporting everything from real-time dashboards to machine learning pipelines.
Azure AI and Machine Learning Capabilities
MS Azure is a leader in democratizing artificial intelligence. Its AI services include pre-built models for vision, speech, language, and decision-making, accessible via APIs. For example, Azure Cognitive Services allow developers to add facial recognition or sentiment analysis to apps without deep AI expertise.
For custom model development, Azure Machine Learning provides a full lifecycle platform for building, training, and deploying models. It integrates with popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn, and supports MLOps for continuous delivery of AI models.
Notable use cases include:
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostics using medical imaging.
- Retail: Personalized recommendations and demand forecasting.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance using IoT sensor data.
Security and Compliance in MS Azure
Security is a top priority for any cloud platform, and MS Azure excels in this area with a defense-in-depth approach. Microsoft invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity and employs more than 3,500 security experts.
Built-in Security Features
Azure provides a suite of native security tools:
- Azure Security Center: Unified security management and advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
- Azure Defender: Extended detection and response (XDR) for servers, containers, and databases.
- Azure Key Vault: Securely stores secrets, keys, and certificates.
- Azure Firewall: Managed, cloud-native network firewall service.
These tools work together to monitor, detect, and respond to threats in real time. For example, Security Center can automatically detect suspicious login attempts and recommend remediation steps.
Compliance and Certifications
MS Azure complies with more than 140 international and industry-specific standards, including:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- ISO/IEC 27001, 27017, 27018
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
This makes Azure a preferred choice for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government. Azure’s Compliance Manager helps organizations assess their compliance posture and generate audit reports.
Identity and Access Management
Azure Active Directory (AAD) is the cornerstone of identity management in MS Azure. It supports multi-factor authentication (MFA), conditional access policies, and identity protection using AI-driven risk detection.
For example, if a user logs in from an unfamiliar location, AAD can prompt for MFA or block the access attempt. It also integrates with on-premises Active Directory via Azure AD Connect, enabling seamless hybrid identity management.
“Security is not a product, but a process. Azure makes that process easier.” — Microsoft Security Blog
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies with MS Azure
Many organizations are not ready—or willing—to move entirely to the public cloud. This is where MS Azure’s hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities shine. Azure enables a smooth transition from on-premises to cloud while maintaining control and flexibility.
Azure Arc: Extending Azure Management Everywhere
Azure Arc allows IT teams to manage servers, Kubernetes clusters, and data services across on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud environments using Azure Resource Manager (ARM). This means you can apply Azure policies, governance, and monitoring to non-Azure resources.
For example, a company running VMs on VMware can register them with Azure Arc and apply security baselines or backup policies from the Azure portal. This unified management reduces complexity and improves operational efficiency.
Azure Stack: Bringing the Cloud On-Premises
Azure Stack is a family of products that brings Azure services into on-premises data centers. It includes:
- Azure Stack Hub: Full-featured platform for service providers and large enterprises.
- Azure Stack Edge: Hardware device with AI capabilities for edge computing.
- Azure Stack HCI: Hyper-converged infrastructure for virtualized workloads.
This is ideal for industries with strict latency, data residency, or regulatory requirements, such as defense, energy, and manufacturing.
Multi-Cloud Integration and Interoperability
While Azure is a powerful standalone platform, it also supports interoperability with other clouds. For example, Azure Red Hat OpenShift allows running Red Hat OpenShift clusters on Azure, and Azure VMware Solution enables migration of VMware workloads without re-architecture.
Additionally, tools like Terraform and Ansible support multi-cloud automation, allowing DevOps teams to manage AWS, GCP, and Azure resources with the same codebase.
Real-World Applications and Industry Use Cases
MS Azure is not just theoretical—it’s being used by organizations worldwide to solve real business challenges. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, Azure powers innovation across sectors.
Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes
Hospitals and clinics use Azure to store and analyze electronic health records (EHR), run AI-powered diagnostics, and enable telemedicine. For example, the UK’s NHS uses Azure to process millions of patient records securely and support remote consultations during pandemics.
Azure Health Data Services integrates FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standards, enabling seamless data exchange between systems.
Finance: Enhancing Security and Scalability
Banks and fintech companies leverage Azure for fraud detection, risk modeling, and customer analytics. JPMorgan Chase, for instance, uses Azure to run complex financial simulations and scale trading platforms during market volatility.
Azure’s compliance with financial regulations ensures data integrity and auditability, while its high availability minimizes downtime during critical operations.
Manufacturing: Driving Smart Factories
Manufacturers use Azure IoT Hub and Azure Digital Twins to create digital replicas of physical assets. This enables predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and process optimization.
Siemens, for example, uses Azure to connect thousands of industrial machines globally, reducing unplanned downtime and improving energy efficiency.
Getting Started with MS Azure: Tips and Best Practices
Starting with MS Azure can be overwhelming due to its vast service catalog. However, following best practices can accelerate adoption and ensure long-term success.
Create a Landing Zone Architecture
A landing zone is a secure, scalable foundation for deploying workloads in Azure. It includes networking, identity, governance, and security policies. Microsoft provides Azure Landing Zone guidance through the Cloud Adoption Framework, helping organizations design their environment correctly from day one.
Key components include:
- Subscription structure (management groups, departments, projects)
- Network topology (hub-spoke model, firewalls)
- Identity and access controls (RBAC, PIM)
- Monitoring and logging (Azure Monitor, Log Analytics)
Leverage Azure Free Tier and Learning Resources
Microsoft offers a free account with $200 credit for 30 days and access to over 25 always-free services. This is perfect for experimentation and learning.
In addition, Microsoft Learn provides free, interactive modules on Azure fundamentals, security, AI, and more. Certifications like AZ-900 (Azure Fundamentals) and AZ-104 (Azure Administrator) are highly valued in the IT industry.
Adopt DevOps and Automation
To maximize efficiency, organizations should adopt DevOps practices using Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like ARM templates and Bicep.
Automation reduces human error, speeds up deployments, and ensures consistency across environments. For example, a CI/CD pipeline can automatically test and deploy a web app to Azure App Service whenever code is pushed to a GitHub repository.
What is MS Azure?
MS Azure is Microsoft’s cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services including virtual machines, storage, databases, AI, and networking. It enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud.
How does MS Azure compare to AWS?
While AWS has a larger market share, MS Azure excels in hybrid cloud integration, enterprise support, and Microsoft ecosystem compatibility. Azure is often preferred by organizations already using Microsoft products.
Is MS Azure secure?
Yes, MS Azure is highly secure, with built-in threat detection, encryption, compliance certifications, and advanced identity management through Azure Active Directory.
Can I use MS Azure for free?
Yes, Microsoft offers a free tier with $200 credit for 30 days and access to many always-free services. You can also use Microsoft Learn for free training.
What industries use MS Azure?
MS Azure is used across healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, education, and government sectors for applications ranging from data analytics to AI and IoT.
MS Azure has firmly established itself as a leader in the cloud computing space. Its powerful combination of scalability, security, hybrid capabilities, and AI integration makes it a top choice for businesses undergoing digital transformation. Whether you’re a developer, IT professional, or business leader, understanding MS Azure’s capabilities is essential for staying competitive in today’s technology-driven world. By leveraging its vast ecosystem and following best practices, organizations can unlock innovation, reduce costs, and deliver better experiences to their customers.
Further Reading: